GROUPS OF ORGANISMS
|
 PLANTS: PLANTS:
Photosynthesis
|
ANIMALS
 Multicellular Organisms Multicellular Organisms
Stores Carbohydrates as Glycogen
Cells DO NOT contain Chloroplasts; cannot carry out photosynthesis
No Cell walls
Nervous Coordination: Can move from one place to another
Example: Mammals and Insects
|
 FUNGI FUNGI
Both Multicellular and Unicellular
Stores Carbohydrates as Glycogen
Cell walls are made of Chitin
DO NOT carry out Photosynthesis
Organised into a Mycelium: Thread-like structure called Hyphae, which contains many Nuclei
They feed by Extracellular Secretion: Releases digestive enzymes onto food and absorb organic products ( saprotrophic nutrition )
Example: Mucor / Yeast
|
 BACTERIA BACTERIA
Unicellular Organisms
Lack in Nuclei’s so has circular chromosomes of DNA called Plasmids
Has Cell wall, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm
SOME can carry out Photosynthesis
Feeds by eating living or dead living Organisms
Example: Lactobacillus Bulgaricus (Yoghurt Production)
|
PROCTISTS
 Microscopic Unicellular Organisms Microscopic Unicellular Organisms
Example: Animals: Amoeba
Plants: Chlorella
|
VIRSUS
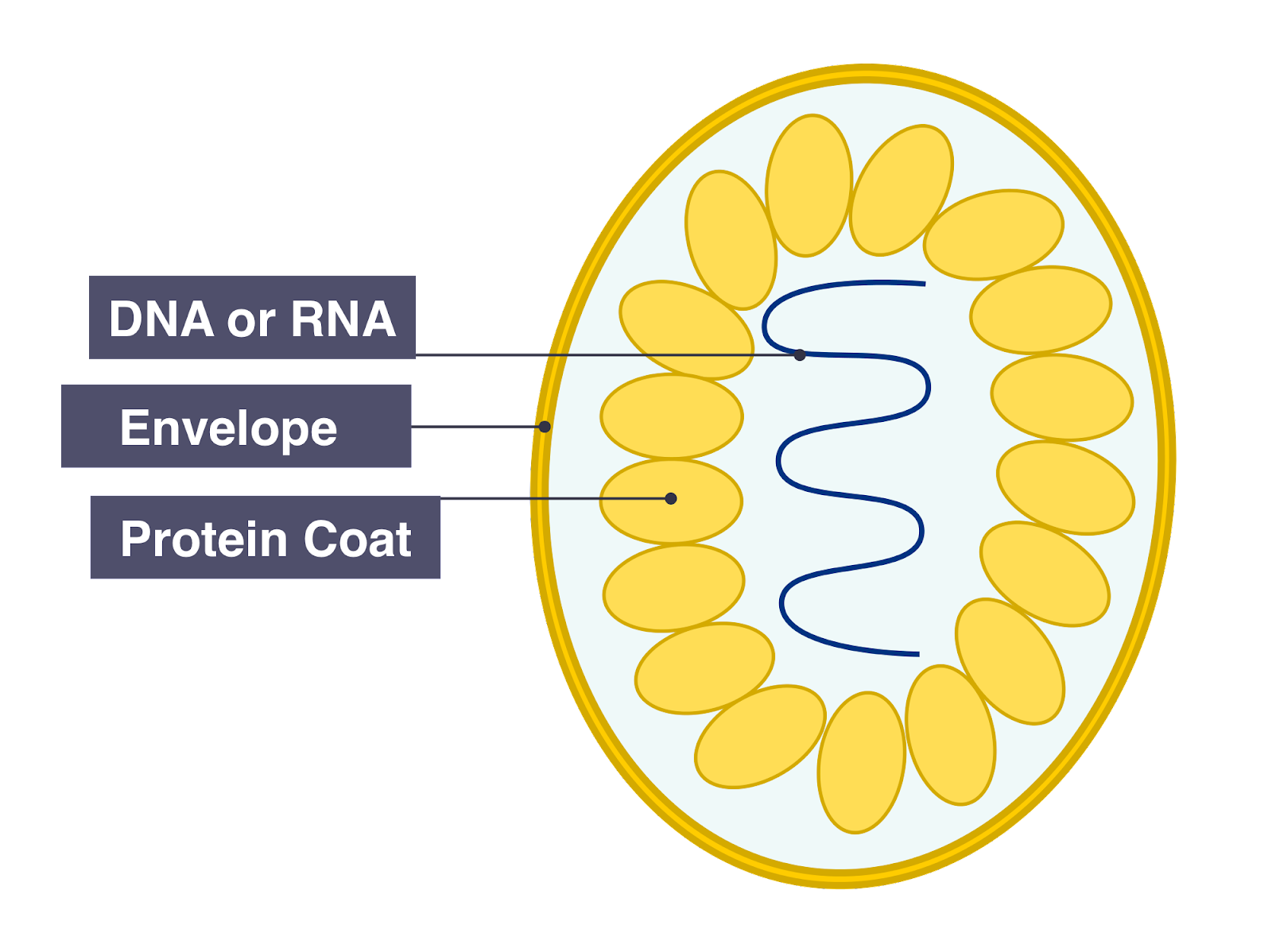 Small Particles ( smaller than Bacteria ) Small Particles ( smaller than Bacteria )
Parasitic: can only reproduce in living Organisms
They only reproduce infect every type of living Organisms
They have a wide variety of shapes and sizes
No Cellular structure
Has protein coat
Contains one type of Nucleic Acid ( RNA or DNA )
Example: Tobacco Mosaic Virus / HIV
Plants: Chlorella
|
huyg
ReplyDeleteomg keisho inoue i <3 u
ReplyDelete